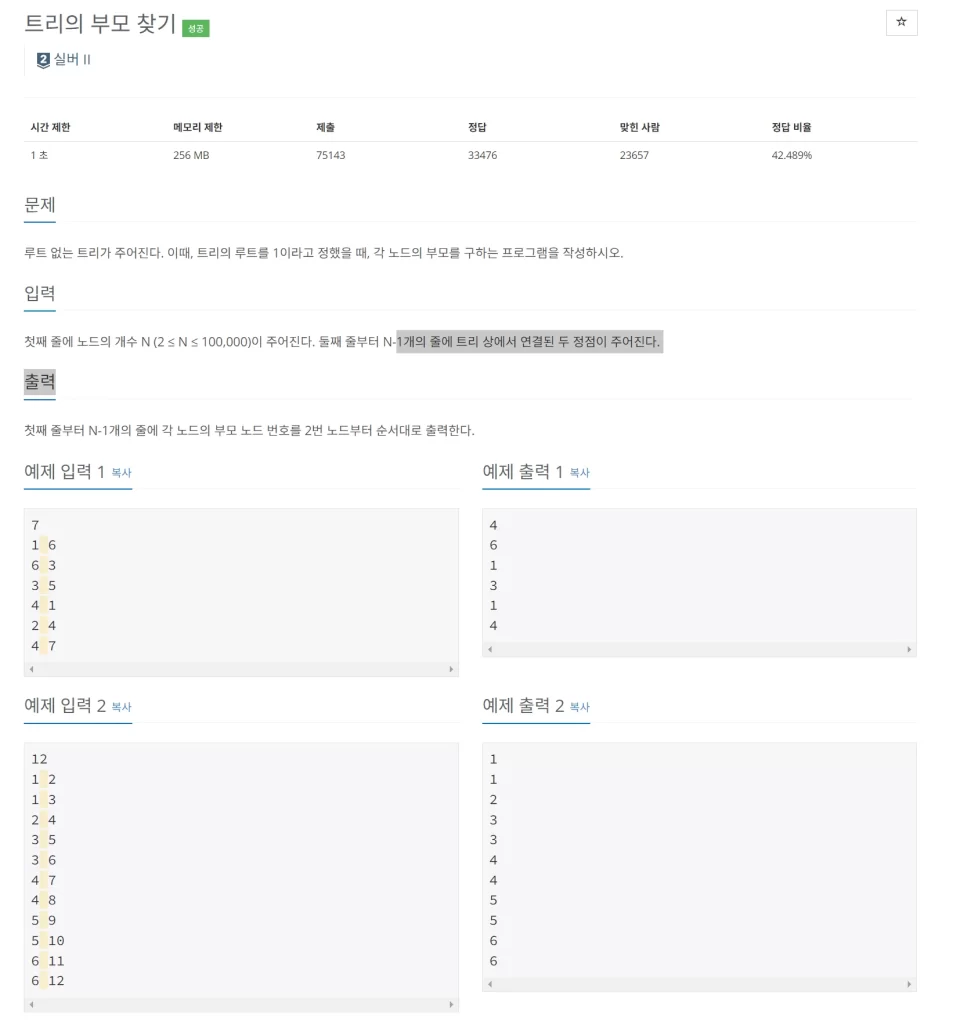
문제 내용은 그래프의 간선을 받은 뒤, 노드의 2번째 정점부터 해당 노드의 부모 노드를 호출해주면 되는데 예제 입력을 보면 1~7까지 정점이 있는데 2부터 시작해서 7까지 진행하되
방문한 순으로 출력하라는게 아니라, 해당 정점의 부모 노드를 호출하라는 얘기다
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Main {
static Map<Integer, ArrayList<Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>();
static HashSet<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();
static int[] location;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int count = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < count - 1; i++) {
int[] edge = Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
graph.putIfAbsent(edge[0], new ArrayList<>());
graph.putIfAbsent(edge[1], new ArrayList<>());
graph.get(edge[0]).add(edge[1]);
graph.get(edge[1]).add(edge[0]);
}
location = new int[count + 1];
bfs();
for (int i = 2; i < location.length; i++) {
System.out.println(location[i]);
}
}
public static void bfs() {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(1);
visited.add(1);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Integer poll = queue.poll();
for (int neighbor : graph.get(poll)) {
if (!visited.contains(neighbor)) {
location[neighbor] = poll;
queue.add(neighbor);
visited.add(neighbor);
}
}
}
}
}문제를 풀어보면 graph 안에 간선을 모두 연결해주고, BFS 진행 전 location[] 배열을 만들고 진행해주되 정점에 연결된 인접 노드들을 호출할 때마다 해당 노드의 부모 노드를 location 배열에 넣어준 후
BFS가 끝나고 나면 2번 노드부터 시작해서 전체 정점 수 만큼 for 문을 진행하면서 해당 노드들의 부모 노드를 호출해주면 끝이다

Leave a Reply